CompeteExperiment¶
There are still many challenges in the machine learning modeling process for tabular data, such as imbalanced data, data drift, poor generalization ability, etc. This challenges cannot be completely solved by pipeline search, so we introduced in HyperGBM a more powerful tool is CompeteExperiment.
CompteExperiment is composed of a series of steps and Pipeline Search is just one step. It also includes advanced steps such as data cleaning, data drift handling, two-stage search, ensemble etc., as shown in the figure below:
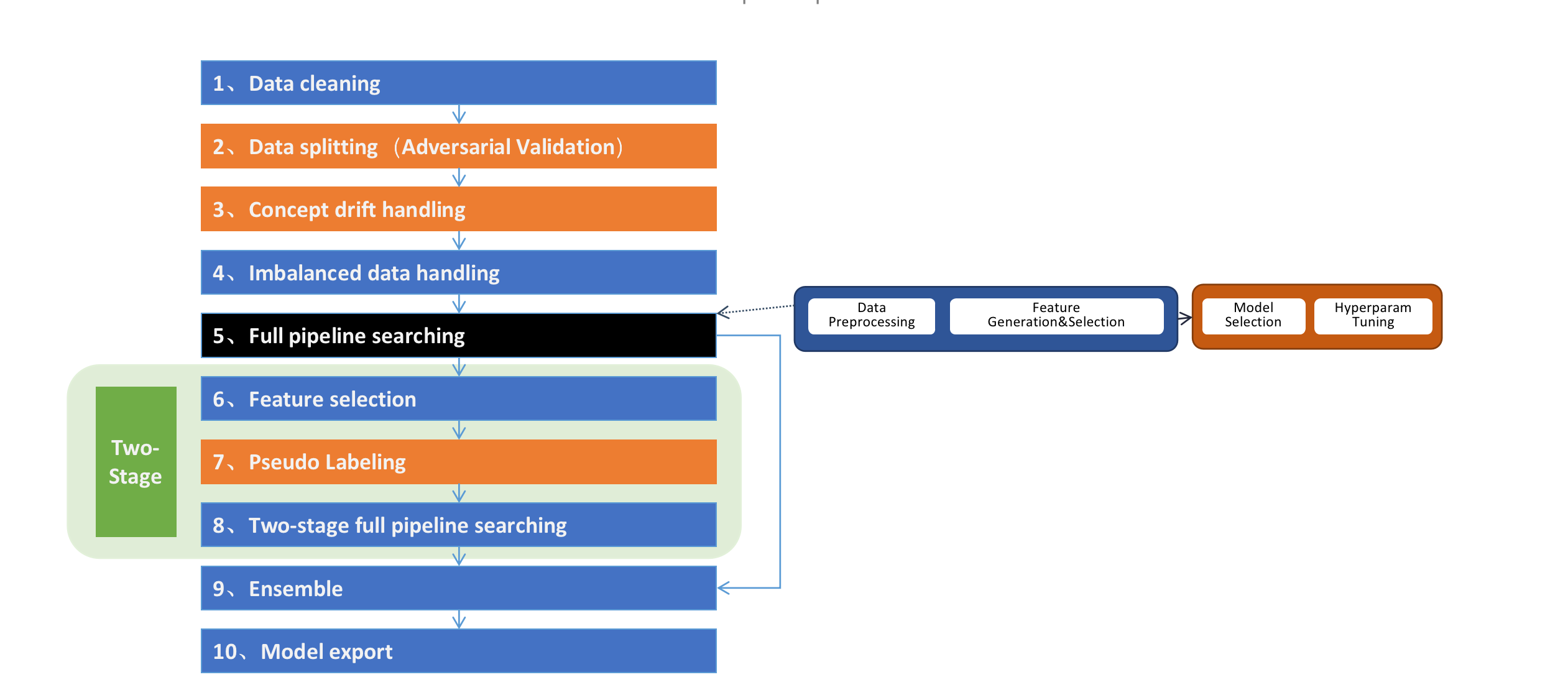
Code example
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypergbm.search_space import search_space_general
import pandas as pd
import logging
# load data into Pandas DataFrame
df = pd.read_csv('[train_data_file]')
target = 'target'
#create an experiment
experiment = make_experiment(df, target=target,
search_space=lambda: search_space_general(class_balancing='SMOTE',n_estimators=300, early_stopping_rounds=10, verbose=0),
collinearity_detection=False,
drift_detection=True,
feature_reselection=False,
feature_reselection_estimator_size=10,
feature_reselection_threshold=1e-5,
ensemble_size=20,
pseudo_labeling=False,
pseudo_labeling_proba_threshold=0.8,
pseudo_labeling_resplit=False,
retrain_on_wholedata=False,
log_level=logging.ERROR,)
#run experiment
estimator = experiment.run()
# predict on real data
pred = estimator.predict(X_real)
Required Parameters
hyper_model: hypergbm.HyperGBM, A
HyperGBMinstanceX_train: Pandas or Dask DataFrame, Feature data for training
y_train: Pandas or Dask Series, Target values for training
Optinal Parameters
X_eval: (Pandas or Dask DataFrame) or None, (default=None), Feature data for evaluation
y_eval: (Pandas or Dask Series) or None, (default=None), Target values for evaluation
X_test: (Pandas or Dask Series) or None, (default=None), Unseen data without target values for semi-supervised learning
eval_size: float or int, (default=None), Only valid when
X_evalory_evalis None. If float, should be between 0.0 and 1.0 and represent the proportion of the dataset to include in the eval split. If int, represents the absolute number of test samples. If None, the value is set to the complement of the train size.train_test_split_strategy: ‘adversarial_validation’ or None, (default=None), Only valid when
X_evalory_evalis None. If None, use eval_size to split the dataset, otherwise use adversarial validation approach.cv: bool, (default=False), If True, use cross-validation instead of evaluation set reward to guide the search process
num_folds: int, (default=3), Number of cross-validated folds, only valid when cv is true
task: str or None, optinal(default=None), Task type(binary, multiclass or regression). If None, inference the type of task automatically
callbacks: list of callback functions or None, (default=None), List of callback functions that are applied at each experiment step. See
hypernets.experiment.ExperimentCallbackfor more information.random_state: int or RandomState instance, (default=9527), Controls the shuffling applied to the data before applying the split.
scorer: str, callable or None, (default=None), Scorer to used for feature importance evaluation and ensemble. It can be a single string (see get_scorer) or a callable (see make_scorer). If None, exception will occur.
data_cleaner_args: dict, (default=None), dictionary of parameters to initialize the
DataCleanerinstance. If None,DataCleanerwill initialized with default values.collinearity_detection: bool, (default=False), Whether to clear multicollinearity features
drift_detection: bool,(default=True), Whether to enable data drift detection and processing. Only valid when X_test is provided. Concept drift in the input data is one of the main challenges. Over time, it will worsen the performance of model on new data. We introduce an adversarial validation approach to concept drift problems in HyperGBM. This approach will detect concept drift and identify the drifted features and process them automatically.
feature_reselection: bool, (default=True), Whether to enable two stage feature selection and searching
feature_reselection_estimator_size: int, (default=10), The number of estimator to evaluate feature importance. Only valid when feature_reselection is True.
feature_reselection_threshold: float, (default=1e-5), The threshold for feature selection. Features with importance below the threshold will be dropped. Only valid when feature_reselection is True.
ensemble_size: int, (default=20), The number of estimator to ensemble. During the AutoML process, a lot of models will be generated with different preprocessing pipelines, different models, and different hyperparameters. Usually selecting some of the models that perform well to ensemble can obtain better generalization ability than just selecting the single best model.
pseudo_labeling: bool, (default=False), Whether to enable pseudo labeling. Pseudo labeling is a semi-supervised learning technique, instead of manually labeling the unlabelled data, we give approximate labels on the basis of the labelled data. Pseudo-labeling can sometimes improve the generalization capabilities of the model.
pseudo_labeling_proba_threshold: float, (default=0.8), Confidence threshold of pseudo-label samples. Only valid when feature_reselection is True.
pseudo_labeling_resplit: bool, (default=False), Whether to re-split the training set and evaluation set after adding pseudo-labeled data. If False, the pseudo-labeled data is only appended to the training set. Only valid when feature_reselection is True.
retrain_on_wholedata: bool, (default=False), Whether to retrain the model with whole data after the search is completed.
log_level: int or None, (default=None), Level of logging, possible values:[logging.CRITICAL, logging.FATAL, logging.ERROR, logging.WARNING, logging.WARN, logging.INFO, logging.DEBUG, logging.NOTSET]