Basic Usages
In this section, we are going to provide an example to show how to train a model using the tool make_experiment. In this example, we use the blood dataset, which is loaded from hypernets.tabular. The columns of this dataset can be shown as follows:
Recency,Frequency,Monetary,Time,Class
2,50,12500,98,1
0,13,3250,28,1
1,16,4000,35,1
2,20,5000,45,1
1,24,6000,77,0
4,4,1000,4,0
...
Create and Run an Experiment
Using the tool make_experiment can create an executable experiment object. The only required parameter of this tool is train_data. Then simply calling the method run of the created experiment object will start training and return a model. Note that if the target column of the data is not y, one needs to manually set it through the parameter target.
An example code:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class')
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
output:
Pipeline(steps=[('data_clean',
DataCleanStep(...),
('estimator',
GreedyEnsemble(...)])
Training will return a Pipeline while the final returned model is a collection of multiple models.
For training data with file extension .csv or .parquet, the experiment can be created through using the data file path directly and make_experiment will load data as DataFrame automatically. For an example:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
train_data = '/path/to/mydata.csv'
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='my_target')
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Set the Number of Search Trials
One can set the max search trial number by adjusting max_trials. The following code sets the max searching time as 100:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', max_trials=100)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Use Cross Validation
Users can apply cross validation in the experiment by manually setting parameter cv. Setting cv=False means the experiment will not apply cross validation but applying train_test_split. On the other hand, when cv=True, the experiment will apply cross validation. And the number of folds can be adjusted through the parameter num_folds, whose default value is 3.
Example code when cv=True:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', cv=True, num_folds=5)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Evaluation dataset
When cv=False, the experiment object will additionally require evaluating its perfomance on the evaluation dataset. This can be done by setting eval_data when creating make_experiment. For example:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
train_data,eval_data=train_test_split(train_data,test_size=0.3)
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', eval_data=eval_data, cv=False)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
If the eval_data is not given, the experiment object will split the train_data to obtain an evaluation dataset, whose size can be adjusted by setting eval_size:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', cv=False, eval_size=0.2)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Set the Evaluation Criterion
The default evaluation criterion of the experiment object for classification task is accuracy, while for regression task is rmse. Other criterions can be set through reward_metric. For example:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', reward_metric='auc')
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Set the Early Stopping
One can set the early stopping strategy with settings of early_stopping_rounds, early_stopping_time_limit and early_stopping_reward.
The following code sets the max searching time as 3 hours:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', max_trials=300, early_stopping_time_limit=3600 * 3)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Choose a Searcher
HyperGBM performs hyperparameter search using the search algorithms provided by Hypernets, which includes EvolutionSearch, MCTSSearcher, and RandomSearcher. One can choose a specific searcher by setting the parameter searcher when using make_experiment.
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', searcher='random')
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Furthermore, you can make a new searcher object for experiment, for an example:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypergbm.search_space import search_space_general
from hypernets.searchers import MCTSSearcher
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
my_searcher = MCTSSearcher(lambda: search_space_general(n_estimators=100),
max_node_space=20,
optimize_direction='max')
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', searcher=my_searcher)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Enable TrialStore
In HyperGBM experiments, one can save trial information into trail store. For the same dataset, HyperGBM will reuse the trial results if it was found from the trial store. Enable trail store with option trial_store.
train_data = ...
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, trial_store='/tmp/trial_store', ...)
Ensemble Models
make_experiment automatically turns on the model ensemble function to achieve a better model. It will ensemble the best 20 models while the number for ensembling can be changed by setting ensemble_size as the following code, where ensemble_size=0 means no ensembling wii be made.
train_data = ...
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, ensemble_size=10, ...)
Set Parallelism
By default, HyperGBM will use all CPUs in the parallel computing. One can control the number of threads or processes with option n_jobs.
train_data = ...
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, n_jobs=10, ...)
Set Log Levels
The progress messages during training can be printed by setting log_level (str or int). Please refer the logging package of python for further details. Besides, more comprehensive messages will be printed when setting verbose as 1.
The following codes sets the log level to ‘INFO’:
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
train_data = dsutils.load_blood()
experiment = make_experiment(train_data, target='Class', log_level='INFO', verbose=1)
estimator = experiment.run()
print(estimator)
Output:
14:24:33 I hypernets.tabular.u._common.py 30 - 2 class detected, {0, 1}, so inferred as a [binary classification] task
14:24:33 I hypergbm.experiment.py 699 - create experiment with ['data_clean', 'drift_detection', 'space_search', 'final_ensemble']
14:24:33 I hypergbm.experiment.py 1262 - make_experiment with train data:(748, 4), test data:None, eval data:None, target:Class
14:24:33 I hypergbm.experiment.py 716 - fit_transform data_clean
14:24:33 I hypergbm.experiment.py 716 - fit_transform drift_detection
14:24:33 I hypergbm.experiment.py 716 - fit_transform space_search
14:24:33 I hypernets.c.meta_learner.py 22 - Initialize Meta Learner: dataset_id:7123e0d8c8bbbac8797ed9e42352dc59
14:24:33 I hypernets.c.callbacks.py 192 -
Trial No:1
--------------------------------------------------------------
(0) estimator_options.hp_or: 0
(1) numeric_imputer_0.strategy: most_frequent
(2) numeric_scaler_optional_0.hp_opt: True
...
14:24:35 I hypergbm.experiment.py 716 - fit_transform final_ensemble
14:24:35 I hypergbm.experiment.py 737 - trained experiment pipeline: ['data_clean', 'estimator']
Pipeline(steps=[('data_clean',
DataCleanStep(...),
('estimator',
GreedyEnsemble(...)
Experiment Visualization
HyperGBM supports user interface based on webpage by setting the argument webui=True, where you see all the processing and parameters information displayed in a dashboard.
Note: This function requires to install hypergbm with the command:
pip install hypergbm[board]
The example codes of enabling experiment visualization based on website is shown below:
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from hypergbm import make_experiment
from hypernets.tabular.datasets import dsutils
df = dsutils.load_bank()
df_train, df_test = train_test_split(df, test_size=0.8, random_state=42)
experiment = make_experiment(df_train, target='y', webui=True)
estimator = experiment.run(max_trials=10)
print(estimator)
The output is:
02-17 19:08:48 I hypernets.t.estimator_detector.py 85 - EstimatorDetector error: GPU Tree Learner was not enabled in this build.
Please recompile with CMake option -DUSE_GPU=1
...
server is running at: 0.0.0.0:8888
...
02-17 19:08:55 I hypernets.t.metrics.py 153 - calc_score ['auc', 'accuracy'], task=binary, pos_label=yes, classes=['no' 'yes'], average=None
final result:{'auc': 0.8913467492260062, 'accuracy': 0.8910699474702792}
Then you could see the experiment progress dashboard by accessing the web server http://localhost:8888. One screenshot is displayed below:
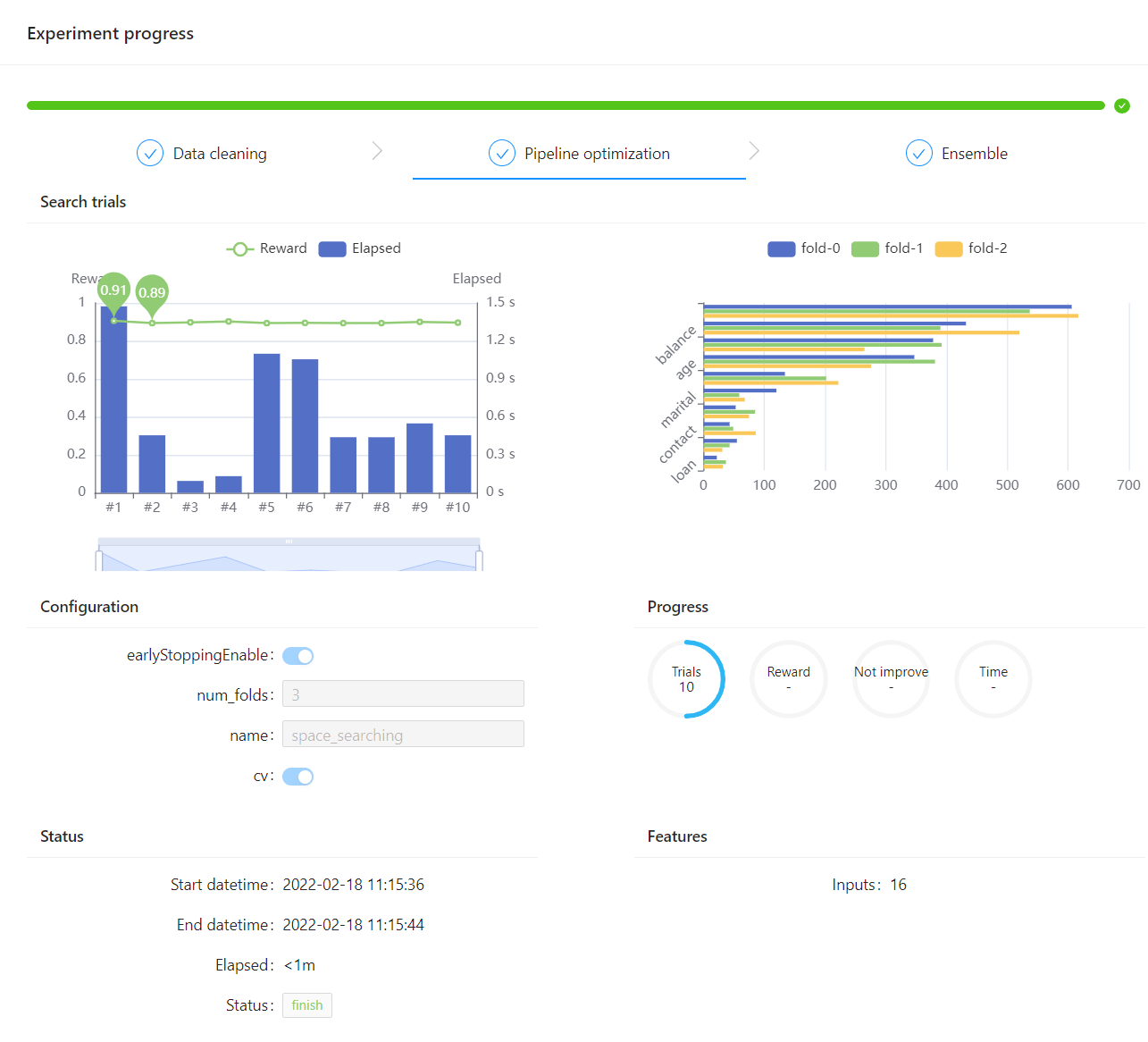
It also support other options to configure the webui: defining the file directory by event_file_dir, setting the server port by server_port, and defining if exiting the web server after finishing the current experiment by exit_web_server_on_finish. See example:
...
webui_options = {
'event_file_dir': "./events", # persist experiment running events log to './events'
'server_port': 8888, # http server port
'exit_web_server_on_finish': False # exit http server after experiment finished
}
experiment = make_experiment(df_train, target='y', webui=True, webui_options=webui_options)
...